分布式系统简介 Introduction to Distributed System
What is a Distributed System?
As defined in Coulouris’book: A distribued system is one in which hardware or software components located at networked computers communicate and coordinate their actions only by passing messages.
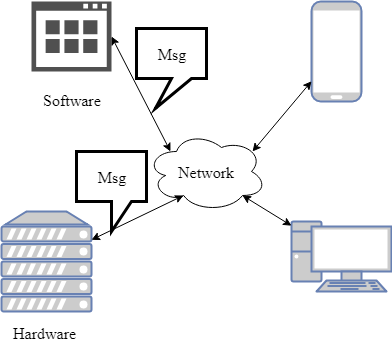
分布式系统的定义:硬件,软件之间通过网络连接,他们之间只通过信息传递来进行工作上的协作和交流。分布式系统是在网络(Network)的基础上搭建的,因此网络本身并不能称之为分布式系统。
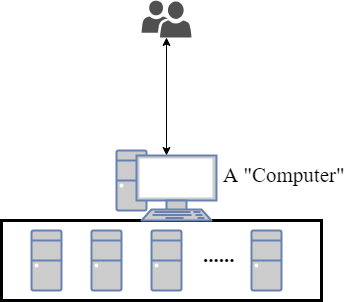
Also, there is another definition by Tanenbaum: A distributed system is a collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single coherent system.
Tanenbaum 给出了另外一个角度的定义:虽然一个分布式系统是由很多独立的电脑组成的,但在用户视角,这就是“一台电脑”(换句话来说,用户并不知道这个系统是由多少台独立的电脑组成的)
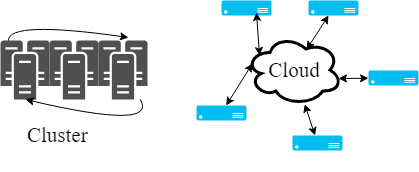
Example of Distributed Systems:
Cluster - a collection of interconnected stand-alone computers cooperatively working together as a single, integrated computing resource.
Cloud - a collection of interconnected and virtualised computers that are dynamically provisioned and presented as one or more unified computing resources based on service-level agreements established through negotiation between the service provider and consumers.
Cloud 和 Cluster 之间的区别是, cluster 内的组件一般是通过LAN (局域网)相连的,而Cloud则是可以做到不受地域限制(Geographically distributed)。Cluster更像是将很多个电脑堆在一起做成一个“大电脑”。
5 Reasons for Distributed System (FIPRE)
-
Functional separation (e.g. Client Server)
分布式系统可以将不同的功能分隔开,降低系统的耦合程度,方便维护。 -
Inherent distribution
维持固有的分布属性。分为Information和People两方面。在不同的网页中,不同的信息是由不同的人来维护的 (Information),而在一些协同工作中,不同的人(如医生,工程师等)可以通过DS来完成作业 (People)。 -
Power imbalance and load variation
-
Reliability
系统的可靠性。数据可以在多个节点上备份。 -
Economies
通过共享来降低资源的拥有成本(reduce cost of ownership),如可以多人共用一个打印机进行作业。
4 Consequences of DS (CHNI)
Concurrency, Heterogenerity, No global clock, Independent failures.
5 Characteristics of DS (PCRNN)
Parallel activities, Communication via message passing, Resource sharing, No global state, no global clock. Global state is useful in multiple situations like distributed garbage collection, deadlock resolution, and distributed termination. These examples can be found in page 628/629 in Coulouris’book.
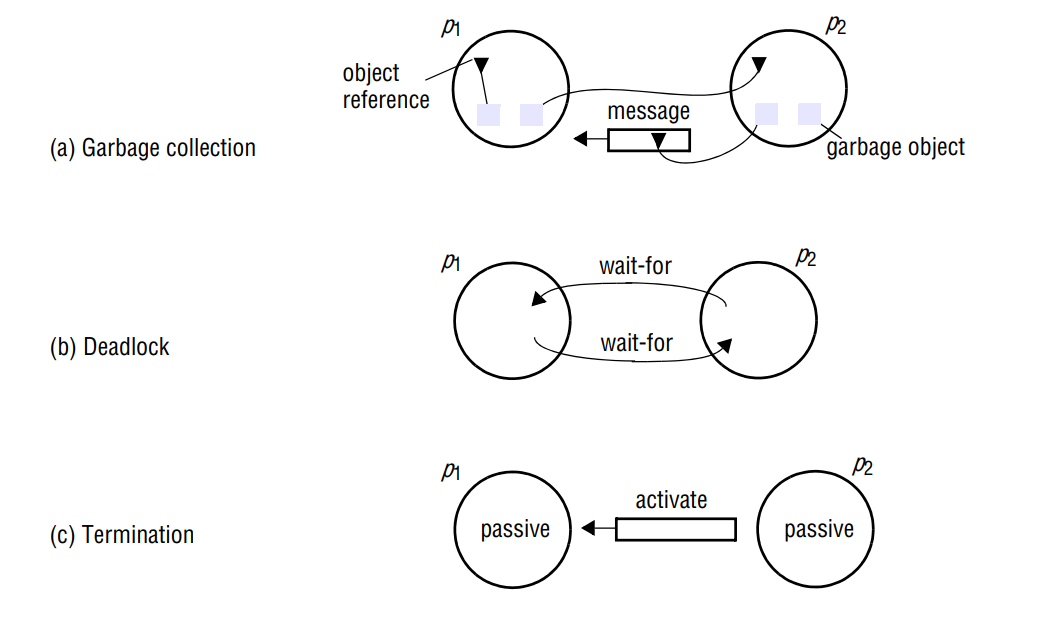 However, due to the absence of global clock, there is no global state in a distributed system.
However, due to the absence of global clock, there is no global state in a distributed system.
一些容易理解的概念就不再赘述了,这里提一下global state这个概念,翻译过来就是系统的一个“全局状态”。分布式系统里因为没有全局时间,因此也没有全局状态。但是两者都非常有用,因此有一些方法来“实现”global state。其中一个非常著名的算法Chandy and Lamport的snapshot算法,有兴趣的可以研读链接里的论文。
5 Goals of DS (CTOSE)
- Connecting user and resources
- Transparency
- Openness
- Scalability
- Enhanced Availability
According to Coulouris, openness determines whether the system can be extended and reimplemented in various ways. 要做到openness这一点,详尽的文档是必不可少的,同时关键的接口(要符合标准)要公开。Openness的定义也可以在这里找到。
7 General challenges for DS
-
Heterogenerity (不同的操作系统,硬件,编程语言,安全系统等应该都可以通过DS协作)
-
9 Distributed transparencies (“分布式” 要尽可能对用户隐藏,包括Access - local资源和remote资源的access是一致的, Location - 如将domain name和machine address分开,Failure,Replicate - 复制的(可能用于data backup)数据对用户是隐藏的, Migration - e.g. 切换不同的name service, Concurrency - 每个process都不知道自己在跟别人share resource, Performance - 根据用户量的增长调整组件/算法等等, Scaling - expand scale时不用改动系统架构/应用算法, Application Level transparencies.)
-
Fault tolerance (不能因为仅仅一个组件炸了导致整个系统崩溃!detection,masking,toleration,recovery)
-
Scalability (1. 随着用户数量增长,系统要保持高效 2. 能够利用新增的资源来提高效率)
-
Concurrency (可以有共享资源)
-
Openness
-
Security (CIA triads + non-repudiation)
 Source: http://www.boblandstrom.com/cia-triad/
Source: http://www.boblandstrom.com/cia-triad/